Every year, Earth Overshoot Day marks a sombre milestone in our relationship with the planet we call home. This critical date signals the moment when humanity’s demand for ecological resources and services surpasses the Earth’s ability to regenerate them for that year. In essence, we have used up our allocated ecological budget by living beyond our means and entering ecological debt. This year, Earth Overshoot Day is on August 2, 2023.
One of the most alarming aspects of Earth Overshoot Day is its consistent advancement each year. Traditionally, the date moves up annually, indicating that we are depleting the Earth’s resources faster than it can replenish them. This trend can be attributed to a combination of factors, including population growth, increased consumption, inefficient resource management, and reliance on fossil fuels.
In 2020, Earth Overshoot Day fell on August 22nd; last year it was July 28; and this year it’s August 2nd. This nonlinear shift in the date serves as a stark reminder of the severity and, most importantly, the fragility and adaptability of the situation. Earth Overshoot Day should never be dismissed as just “another Earth Day.” On the other hand, this also means that if we start now, there is still something we can positively do for the environment and Earth’s resources.
The Birth of Earth Overshoot Day
The concept of Earth Overshoot Day was founded by the Global Footprint Network, an international sustainability organisation. In the late 1980s, a group of researchers, led by Dr. Mathis Wackernagel and Dr. William Rees, developed the Ecological Footprint, a metric used to quantify the ecological impact of human activities. The Ecological Footprint measures the amount of biologically productive land and sea area required to support an individual, a community, or humanity as a whole while accounting for resource consumption and waste assimilation.
In 2006, the Global Footprint Network introduced Earth Overshoot Day as a symbolic date to illustrate the point at which humanity starts living beyond its ecological means. It serves as a global sustainability awareness campaign, urging individuals, governments, and businesses to reflect on their consumption patterns and take action to reduce their ecological footprint.
The Significance of Earth Overshoot Day
Earth Overshoot Day is a critical reminder of the ecological debt crisis we face. When we surpass the planet’s capacity to regenerate its resources, we enter a state of ecological overshoot, essentially borrowing resources from future generations. This overshoot leads to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, soil degradation, water scarcity, and an increase in carbon emissions, accelerating climate change and disrupting ecosystems. The baseline is that overshooting our planet’s limits is not a sustainable path for humanity. As the Earth’s resources are finite, continual overshoot will inevitably lead to ecological collapse, threatening our well-being, prosperity, and even survival. It is crucial to understand that living beyond our means ecologically is no different from living beyond our financial means; both lead to detrimental consequences.
Recognising the significance of Earth Overshoot Day can serve as a wake-up call for governments, organisations, and individuals to take urgent action. It prompts us to reassess and modify our lifestyles, consumption patterns, and economic models to achieve a more sustainable and equitable world.
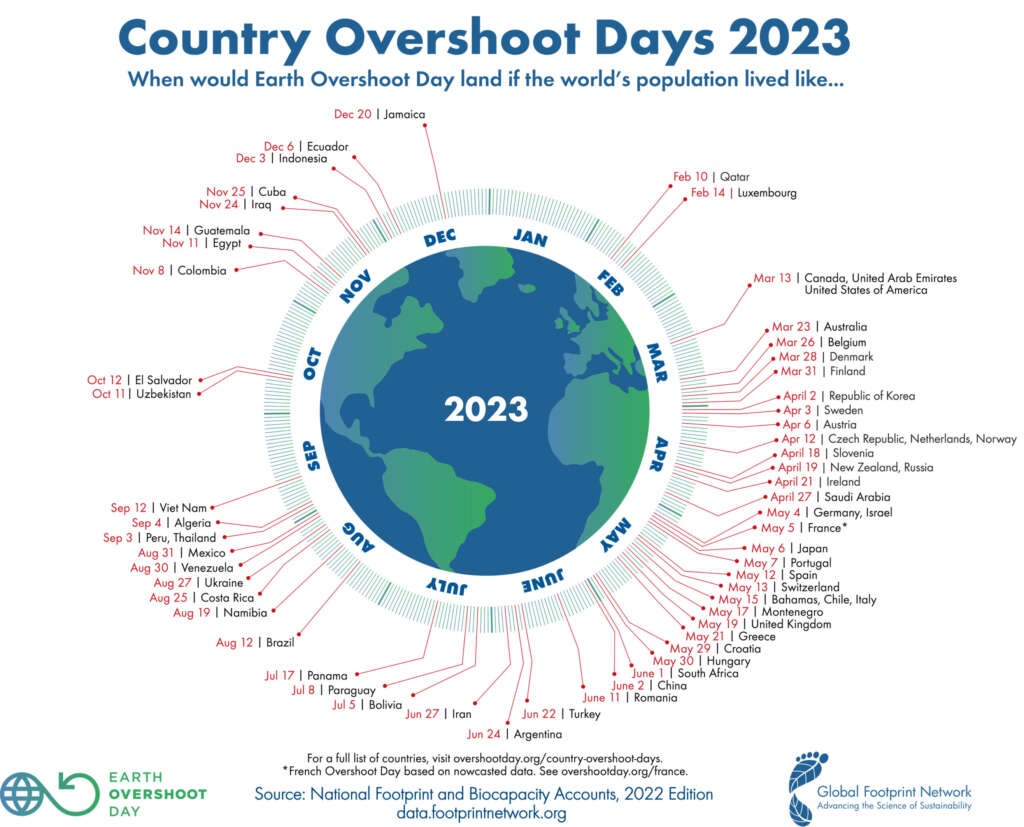
It’s also important to note that each country has its own unique Overshoot Day due to variations in biocapacity and ecological footprint. When a country’s ecological resource demand surpasses its biocapacity, it experiences an ecological deficit and an earlier Overshoot Day.
The Impact of Earth Overshoot Day on Daily Life
Earth Overshoot Day may seem like an abstract concept, but its effects are tangible in our daily lives. From the food we eat, the water we drink, and the air we breathe to the stability of our climate, everything is interconnected with the health of our planet.
Resource Scarcity
The effects of resource depletion are felt in various ways: rising prices of essential goods such as food and water, increasing energy costs, and heightened competition for limited resources. Additionally, scarcity fosters conflicts over access to resources, exacerbating geopolitical tensions.
Energy Costs
The rising energy costs due to resource depletion and environmental degradation lead to higher expenses for electricity, transportation, and goods. Consequently, individuals and businesses face economic challenges that affect disposable income, job opportunities, and overall well-being. Additionally, higher energy costs can limit access to essential services like healthcare, education, and transportation, disproportionately impacting vulnerable communities.
To address this, a shift towards sustainable energy sources and energy-efficient practices is imperative. Reducing our energy consumption and adopting renewable energy alternatives can help mitigate the adverse effects of Earth Overshoot Day and ensure a more sustainable future for everyone.
Economic Impact
As resources become scarcer, their prices rise, leading to higher costs for essential goods and services like food, energy, and water. This can strain household budgets, limit access to basic necessities, and potentially lead to social unrest. Moreover, industries reliant on natural resources face increased production costs, impacting employment and economic growth. Additionally, ecological imbalances resulting from overshoot, such as climate change and habitat destruction, pose further economic risks through extreme weather events, health issues, and damage to infrastructure.
These are just the tips of the iceberg of how Overshoot Day affects us daily. Not to be pessimistic, but I don’t think we want to push it and experience more of the consequences if we don’t act quickly and consistently.
The Circular Economy Approach

By adopting a circular economy approach, where waste is minimised, resources are conserved, and environmental impact is reduced, we can hope to slow down and eventually reverse the trend of Earth Overshoot Day moving earlier each year.
The circular economy is a revolutionary economic model that aims to decouple economic growth from resource consumption and environmental degradation. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows the “take, make, dispose” pattern, the circular economy promotes a closed-loop system of continuous resource use and regeneration. It encompasses principles such as recycling, remanufacturing, refurbishing, and the sharing economy to minimise waste, conserve resources, and extend the life of products.
Waste Minimisation
One of the cornerstones of the circular economy is waste reduction. Instead of allowing resources to end up in landfills, the circular economy encourages recycling and upcycling to reintroduce materials into the production cycle. This drastically reduces the demand for raw materials and lowers the pressure on Earth’s finite resources.
Remanufacturing and Refurbishing
Remanufacturing and refurbishing are essential processes to maximise resource efficiency and reduce waste. Remanufacturing involves disassembling used products, replacing worn-out components, and reassembling them to their original specifications, extending their lifespan and performance, while refurbishing focuses on restoring used products to a functional state without altering their original design. Both methods prioritise recycling and reusing materials, reducing the demand for new resources and minimising environmental impact.
By promoting these practices, the circular economy encourages sustainable production and consumption patterns, creating a closed-loop system that fosters economic growth while preserving the environment.
#LittleGreenSteps
But we’re not at a dead end. Amidst the dire crisis of Earth Overshoot Day, hope shines through innovative solutions. By embracing sustainable practices, conserving resources, promoting renewable energy, and fostering global cooperation, we can work together to reverse the trend. Every individual’s actions matter; a collective effort can lead us towards a more balanced and resilient future.
To address the ecological debt crisis and prevent Earth Overshoot Day from moving up faster each year, individuals, communities, and governments can take proactive steps:
- Promote Sustainable Consumption: Reduce, reuse, and recycle to minimise waste and the demand for resources.
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Embrace solar, wind, hydro, and other renewable energy sources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Support Sustainable Agriculture: Choose organic and locally produced foods to reduce the ecological impact of agriculture.
- Preserve Forests: Support and participate in initiatives that protect and restore forests, which act as carbon sinks and maintain biodiversity.
- Invest in Green Technologies: Support and invest in the research and development of sustainable technologies that can replace harmful practices.
- Advocate for Policy Changes: Urge governments to implement policies that incentivize sustainable practices and penalise environmentally damaging activities.
- Raise Awareness: Educate others about the ecological consequences of overshooting and inspire them to take action.
- Reduce your carbon footprint by walking, biking, carpooling, or using public transportation instead of relying on individual cars.
- Conserve Water: Use water efficiently and be mindful of water-intensive activities.
- Support Sustainable Brands: Choose products from companies that prioritise sustainability and ethical practices.
Earth Overshoot Day is an urgent and powerful call to action for humanity to address the ecological debt crisis and adopt sustainable practices. The advancement of this date each year underscores the critical need for change. By taking collective and individual actions to reduce our ecological footprint, we can ensure a more sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come. Embracing sustainable practices is not a choice; it is an imperative for the survival of our planet and all its inhabitants. Let us work together to preserve and protect the delicate balance of nature and secure a thriving and resilient world for ourselves and future generations.
FEATURED IMAGE BY Jeff J Mitchell/Getty Images

